How To Install Processmaker
Download Instant Removal Tool Tested Malware & Virus Free by McAfee ProcessMaker, a software developed by Colosa, often gets into your computer via Webpage browse or some freeware’s installation. To safely remove the program, the wrong way is to locate its folder, right-click it and select “Delete”, while quite a number of people are still doing this. Haste makes waste. Every proper removal requires sequential steps. If you recklessly delete whatever you consider redundant, undesirable effects may show up one after another, such as. Error message “The program was not properly or completely installed.”. The system is unable to activate the default uninstaller of the ProcessMaker.
ProcessMaker, a software developed by Colosa, often gets into your computer via Webpage browse or some freeware’s installation. To safely remove the program, the.
Some necessary files are missing or deleted. One or more registry entries of the program are corrupted. You are told that your computer may have been infected with virus, and the system can’t normally function. Program Details ProcessMaker program is developed by the company named Colosa.
The official website of the developer is www.processmaker.com. Normally the program size is around. The default installation directory of the program is. The default uninstaller of the program is C: users user appdata Roaming ProcessMaker-2042 uninstall.exe. Among all its users globally, 77.78% are from United States,the program is also popular in the countries of Germany and CY.
Users with the percentage of 77.78% run this program on the operating system of Windows 7. Detailed information about ProcessMaker program. Program Directory: C: users user appdata Roaming ProcessMaker-2042. Default Uninstaller: C: users user appdata Roaming ProcessMaker-2042 uninstall.exe. Program official website: www.processmaker.com (“X” stands for the hard drive you install ProcessMaker on.) How to delete ProcessMaker You may not notice there would still be leftovers of ProcessMaker, for example, some read-only files automatically kept by the system or its registry entries, staying right in your drive, even if you have gone through correct process via Control Panel or its default uninstaller.
It is required you to carefully remove related items in Registry Editor to accomplish the job, which is risky in some degree. Things could get worse if you mistakenly delete those needed by system running. To safely remove ProcessMaker, we recommend this reliable third-party tool for your reference. Easy steps to remove ProcessMakerwith the removal tool. United States. 35.00%.
Germany. 10.00%. CY. 5.00%. Thailand.
5.00%. Colombia.
5.00%. Belgium. 5.00%.
France. 5.00%. RS. 5.00%. Greece.
5.00%. Japan. 5.00%. Iran. 5.00%. SC. 5.00%.
United Arab Emirates. 5.00% Don’t forget ProcessMaker’s leftovers Again, like I mentioned previously, after ProcessMaker is successfully kicked out of your computer, you still get to manually get rid of the idle leftovers including registry entries, cache files, and temporary files, etc. It is not that easy to precisely track down those little “pieces” since they may not be named with “ProcessMaker” prefix. Sometimes you need to acquire the name of relevant verified publisher first to locate the keys in Registry Editor. It is better not to go there unless you are 100% sure you have targeted the right things, because they will not return once being eliminated.
Solution: Try this well-designed uninstaller to remove ProcessMaker once and for all, with which there will be no need to worry about the current or future invasion of any PUP (Potential Unwanted Program). You PC performance can be greatly optimized through cleaning either hard drives or the Registry. Click the button below to download the tool.
. This guide provides instructions on how to manually install and configure the following ProcessMaker versions on a Windows platform: ProcessMaker 3.0 - 3.1.0.8 ProcessMaker 3.1 - 3.1.3 ProcessMaker 3.2 - 3.2.1 Before installing ProcessMaker, check the of your version of ProcessMaker to see whether your server meets the necessary hardware and software requirements. Also, do not forget to read the following recommendations: Recommendations. Check our Supported Stacks page and the List for, and.
To use ProcessMaker with Internet Explorer 11, please read the page. ProcessMaker is not compatible with, which is enabled by default in MySQL 5.7. Read the section to learn how to disable it. Since MySQL 5.7 is NOT part of any official ProcessMaker stack, ProcessMaker has not been tested entirely in this version of MySQL. Therefore, ProcessMaker may not run correctly even if STRICT mode is disabled. Manual Installation Note: To install ProcessMaker 3.0.1.8, 3.1.x or 3.2.x on Windows Server 2012 R2, please follow the instructions on the page to install Apache, MySQL and PHP. Then, continue with and the following steps in this guide.
Step 1: Installing the Apache Server Download the Apache 2.4 binary file VC11 (available in x64 or x86) from this page. The Apache binary file must be compiled with the VC redistributable compiler. In the case Apache 2.4 VC11 must be compiled with C Redistributable Visual Studio 2012, go to the page. Select the language and click on the Download button. Select the vcredistx64 or vcredistx86 file (depending on your system) and click on the Next button in the bottom right corner of the dialog screen.
The file will begin downloading automatically. Once the file has finished downloading, install the 'vcredistx XX.exe' file as the administrator.
The window shown in the image below will be displayed. Check the box to accept the installation terms and conditions, and click on Install to begin the installation. Extract the Apache binary file (if the x64 bit version was downloaded, the file is named 'httpd-2.4.20-win64-VC11.zip') to the disk C:. There is an Apache24 folder inside it. Cut and paste the Apache24 folder into C:. Note that decompressing the binary file in another location will require extra configuration, because the default ServerRoot path in Apache's conf files is: C: Apache24.
Edit the Apache file httpd.conf located at C: Apache24 conf httpd.conf Uncomment the following modules (remove the # symbol at the beginning of each line). LoadModule authnzldapmodule modules /modauthnzldap.so LoadModule deflatemodule modules /moddeflate.so LoadModule expiresmodule modules /modexpires.so LoadModule ldapmodule modules /modldap.so LoadModule rewritemodule modules /modrewrite.so LoadModule sslmodule modules /modssl.so LoadModule vhostaliasmodule modules /modvhostalias.so LoadModule filtermodule modules /modfilter.so By default, the httpd.conf file is configured to listen to all addresses on the machine on port 80. However, it may need to be configured to listen on specific ports, or only to selected addresses depending on your server.
LoadModule php5module 'C: php php5apache24.dll' AddType application/x-httpd-php.php # configure the path to php.ini PHPIniDir 'C: php php.ini' Save the changes and close the file. Step 2: Installing PHP PHP Restrictions Please take notice of the following PHP restrictions:.
ProcessMaker does NOT support PHP 7. On some hosted servers, the and functions may be disabled, which will cause ProcessMaker's API not to work properly since REstler library uses those functions. Make sure those functions are enabled. Windows Operating System x86 only supports 32-bit timestamps. The valid range of a 32-bit timestamp is typically from Fri, 13 Dec 1901 20:45:54 UTC to Tue, 19 Jan 2038 03:14:07 UTC; using out of range values may cause issues. For more information about this problem, go.
Experimental x64 builds of PHP 5 in Windows x86 do not provide 64-bit integer or large file support. Prior to PHP 5.1.0, not all platforms support negative timestamps, therefore your date range may be limited to no earlier than the Unix epoch. This means that dates prior to Jan 1, 1970 will not work on Windows, some Linux distributions, and a few other operating systems. For Windows Operating Systems x64 with 64-bit versions of PHP, the valid range of a timestamp is effectively infinite, as 64 bits can represent approximately 293 billion years in either direction.
Downloading & Configuring PHP Go to the page, scroll down and search for the PHP 5.5. 38.zip installer (choose the x86 or x64 bit version depending on your system) and download the Thread Safe version. PHP has to be thread-safe to be able to work correctly with Apache. First, create a folder named 'php' in disk C: and decompress the php-5.5. 38-Win32-VC11- xXX file inside. Then, rename the file named php.ini-development to php.ini. Open the new php.ini file with your favorite editor, search for the following lines and edit them using the following configuration: shortopentag = On memorylimit = 512M errorreporting = EALL & EDEPRECATED & ESTRICT displayerrors = Off postmaxsize = 24M uploadmaxfilesize = 24M extensiondir = 'C: php ext' Next, uncomment the following extensions (remove the semicolon; at the beginning of each line).
Extension=phpcurl.dll extension=phpgd2.dll extension=phpldap.dll extension=phpmbstring.dll extension=phpmysql.dll extension=phpmysqli.dll extension=phpopenssl.dll extension=phppdomysql.dll extension=phpsoap.dll Save the changes and close the file. Finally, copy the following files located at C: php and paste them to the C: Windows system32 and C: Windows SysWOW64 folders:.
libeay32.dll. libsasl.dll. libssh2.dll.
ssleay32.dll Adding PHP as an Environment Variable To ensure Windows can run PHP tasks from the Windows command prompt, add the PHP installation location to the PATH variable of your Windows server. To do this, display the Start menu, right click on the Computer option, and select the Properties option in the menu. The System window will open. Click the Advanced system settings link that is on the left side of the window. In the System Properties window that is displayed, select the Advanced tab and click on the Environment Variables.
The Environment Variables window will be displayed. Search for the Path variable in the System Variables section. Select it and click on Edit.
A new dialog window will be displayed. Add a semi-colon (;) to the end of the variable value string, then add the file system path of the PHP installation, which in this case is C: php. Click OK to close all the windows.
To test if the PHP path was added successfully, open a command prompt and run php -v to see the version of the PHP installed. Step 3: Installing the MySQL Server Warning: ProcessMaker is not compatible with, which is enabled by default in MySQL 5.7. Read the section to learn how to disable it. Since MySQL 5.7 is NOT part of any official ProcessMaker stack, ProcessMaker has not been tested entirely in this version of MySQL.
Therefore, ProcessMaker may not run correctly even if STRICT mode is disabled. Download the MySQL 5.5. X installer from the.
After selecting your system version, the next page will ask for your registration, but this can be bypassed by clicking the » No thanks, just take me to the downloads button at the bottom. After the installer has been downloaded, double-click on it to start the Setup Wizard.
In the next dialog window, accept the License Agreement and click on Next. In the Setup Type selection dialog, select Complete and continue with the installation. The wizard will be ready to install the MySQL Server. Click on Install to proceed with the installation.
Once the server is installed, check the box to launch the MySQL Instance Configuration Wizard and click on Finish. The Server Instance Configuration Wizard will help automate the process of configuring the server. Click on Next to begin. There are two configuration types available: Detailed Configuration and Standard Configuration. Select the Detailed Configuration option to configure all possible settings then click on the Next button. The Server Type dialog will be displayed.
Select Server Machine, since this option allows the MySQL server to run alongside other server applications, such as FTP, email, and web servers. The MySQL server will be configured to use a moderate portion of the system resources. Next, in the Database Usage dialog select the Transactional Database Only option. This option determines whether the InnoDB storage engine is available and what percentage of the server resources are available to InnoDB.
Some servers need to locate the InnoDB tablespace files in a location other than the MySQL server data directory. If this is the case, in the next dialog place the tablespace files in a separate location. In the next dialog, to prevent the server from running out of resources, choose your preferred option to limit the number of concurrent connections that can be established. Then, enable or disable TCP/IP networking and configure the port number that will be used to connect to the MySQL server. Port 3306 is used by default. If the port number you choose is in use, you are prompted to confirm your choice of port number.
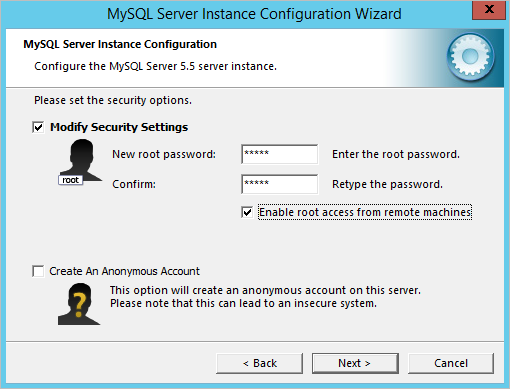
Do not forget to uncheck the box next to the Strict Mode option, since ProcessMaker does NOT support MYSQL strict mode. Favaloro University. Next, select the option Best Support For Multilingualism to support UTF8 as the default server character set.
This is a Unicode character set that can store characters from many different languages. Check both boxes to set the MySQL server as a Windows service and click on Next. If this configuration is used, the MySQL server can be started automatically during system startup, and even restarted automatically by Windows in the event of a service failure.
In the next dialog window, set a root password for the MySQL server installation. ProcessMaker does NOT support special characters (such as: @ # $% ^ & ( /) in the root password. For more information, please read this.
Check the box next to the Enable root access from remote machines option to permit root logins from across the network. Finally, make sure everything is in order and start the configuration process by clicking the Execute button. After the MySQL Server Instance Configuration Wizard has completed its tasks, it will display a configuration summary.
Click the Finish button to exit the MySQL Server Configuration Wizard. Step 4: Download & Extract ProcessMaker Create the folder where ProcessMaker will be installed. For example, create a folder named 'opt' on the disk C:. Download the most recent ProcessMaker tar.gz file from page.
ProcessMaker versions are labeled according to their build number. To download the latest version of ProcessMaker, look for the highest version number. At the moment, the latest version is ProcessMaker 3.2.1. Once the file has been downloaded, open it with your favorite file archiver, such as.
If using 7zip, open the tar.gz file and in the window that opens, click the Extract option. Button to display the Browser for Folder window, and search for the folder created. Select it and click OK. The location selected will be displayed in the Copy to: field.
Click OK to begin the extraction process. The content of the tar.gz file will be extracted to C:/opt. Once the process is completed, all ProcessMaker files will be located in the opt folder. Keep note of this location. Step 5: Apache Configuration The next step is to add the ProcessMaker Virtual Host file to the Apache Virtual Host configuration. To do this, copy the file C: opt processmaker pmos.conf.example to C: Apache24 conf extra and rename it from pmos.conf.example to pmos.conf.
Edit the file C: Apache24 conf httpd.conf and add the following line at the end of the file. ProcessMaker is installed in the /opt/pm3.0.1.7 directory at the IP address 123.45.67.89 and the domains www.example.com and any variant of X.example.com: #processmaker virtual host ServerName 'www.example.com' ServerAlias '.example.com' DocumentRoot C: opt pm3.0.1.7 processmaker workflow publichtml. Note that www.example.com and.example.com need to be defined in the server's DNS or c: Windows System32 Drivers etc hosts file for this example to work correctly. Step 6: Starting Apache Open a command line prompt and enter the following commands to install and start Apache with the new configuration. C: Apache24 bin httpd -k install C: Apache24 bin httpd -k start Step 7: Setting up ProcessMaker Once all ProcessMaker configurations are set up, open a web browser and enter the IP address (and port number if not using the default port 80) where ProcessMaker is installed.
Install Process Hacker
For instance, if ProcessMaker is installed at the address 192.168.10.100, go to or if it is installed locally at port 8080, go to Then, in the web browser, use the installation wizard to complete the installation of ProcessMaker. The wizard should work on any type of computer that is capable of running Apache, PHP and MySQL. Pre-Installation Check The first step in the installation wizard checks whether the server meets ProcessMaker's installation requirements: This step checks the versions of PHP, MySQL and cURL and ensures that the necessary PHP modules are enabled and PHP memorylimit is at least 80MB. Requirements that are not met will be marked as No. Fix any missing requirements before continuing with the installation.
File Permissions The second step of the installation wizard lists the paths of the directories where ProcessMaker stores its files and checks whether those directories have the correct file permissions: If there is a problem accessing some files or directories, check to make sure the file permissions of the directories are set so the Apache user running ProcessMaker can access them. It is possible to change the location of the shared directory, where files containing process and case data are stored. This directory is placed inside the ProcessMaker installation directory under shared by default, but it can be placed in another location or on a Network Address Translation (NAT) server.
If the default location for the shared directory is not used, make sure that the chosen location has the proper file permissions so that it can be accessed by ProcessMaker, but is still restricted from normal users on the server who shouldn't have access to sensitive files. It is recommended to regularly backup the shared directory and MySQL files to prevent data loss. ProcessMaker Open Source License The third step of the installation wizard displays the ProcessMaker license. Mark the option I agree and click on Next to continue the installation. Database Configuration The fourth step of the installation wizard configures the connection to the MySQL database. Enter the name and password of a MySQL user, such as the root user, who has permission to set up new databases in MySQL.
Then click on Test Connection to see whether that user can log in to MySQL and set up the ProcessMaker databases. If ProcessMaker can't connect to MySQL, cannot log in with the user's credentials, or if the database already exists, an error message will appear. Edit the information in the database configuration and click on Test Connection again. Workspace Configuration The last step of the installation wizard configures the username and password of the Administrator user, which are both 'admin' by default. The “admin” user will be able to access all the features and functionalities in the ProcessMaker installation, such as: system configuration, process creation and editing, user and group management, case management, and report and dashboard oversight, among others. Thus, it is strongly recommended to create a strong password for this account.
Take a look at this list of. Also consider using a strong password generator like. The ProcessMaker and its database can also be configured in this step. The name of the workspace can be changed from the default, which is 'workflow'. It may be useful to set up separate workspaces for each department, or division in an organization or for separate sets of processes. By default, the installation wizard will create a new MySQL user who will be granted access to a new database named 'wfworkflow' that will store ProcessMaker data. To use the existing MySQL user from Step 3 instead of creating a new user, mark the Use the current user as the database owner option.
To change the name of the database, mark the Change database name option and write the name in the field under the checkbox. Then click on the Check workspace Configuration button to verify that the configuration is correct. The message ' The configuration is correct.'
Will be displayed and the Finish button will be enabled. If there is an error in the configuration, the message ' Not passed.' Will be displayed in the dialog. For example, if a database of the same name already exists, an error message will be displayed in the bottom right corner. In this case, mark the option Change database name and enter a different name for the database that will be created by ProcessMaker, or mark the option Delete Database if it exists: When the configuration is correct, click on the Finish button to create the workspace database.
If there are no problems, the message 'ProcessMaker was successfully installed' will be displayed. If there was a problem creating the database an error message will be displayed. In this case, check the.
If there was a problem writing the ProcessMaker files, change the file permissions of the directories to give Apache access. First Login Once ProcessMaker has been successfully installed, the web browser will be redirected to the login page. The Get Started screen will appear: To avoid seeing the Get Started screen at every subsequent login, mark the option Don't show me again.
Then, enter the username and password of the Administrator user, which is 'admin' by default, but a different username could have been configured in Step 4 of the installation wizard. Enter the name of the workspace that was configured in Step 4, which is named 'workflow' by default, then click on Login to enter processmaker. The login page can be customized. For more information see.
Note: If a previous version of ProcessMaker was accessed by the web browser unintentionally, it is recommended to after installing ProcessMaker to clear any stored pages from previous versions of ProcessMaker. Step 8: env.ini Configuration Once ProcessMaker is installed, some additional parameters must be set in the main.
Processmaker Tutorial
To do this, edit the env.ini file located at /processmaker/workflow/engine/config/env.ini with a plain text editor. Add the following lines: displayerrors = Off memorylimit = 512M ( the same value set in ) Save changes and restart Apache. Potential Problems Disabling MySQL STRICT Mode MySQL can not use STRICT mode with ProcessMaker. If STRICT mode is enabled, then the following error message will appear when trying to login to ProcessMaker for the first time: ERROR: User does not have rights on this page. To check if MySQL is configured to use strict mode, open the file my.cnf with a plain text editor and look for the following line.
Sqlmode=' Note: Search for a line that contains STRICTALLTABLES mode, and then disable it. In general remove all the lines with STRICTTRANSTABLES, STRICTALLTABLES, and other SQL modes that may be valid in the specific MySQL configuration because they enable the STRICT mode. Then, restart MySQL or reboot for the new configuration to take effect. If ProcessMaker has already been installed, then you will need to delete the existing wfworkflow database in MySQL and reinstall. To do this, first log in to MySQL as the root user from the command line: cd C: MySQL installation directory mysql bin mysql -u root -p Enter the root password for MySQL.
Processmaker Templates
Once in MySQL, drop the wfworkflow database (or whatever name it was given during installation). Mysql drop database wfworkflow; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.59 sec) mysql exit Bye Then, redirect your web browser to your server's location and follow the. MySQL Password with Special Characters The following error is displayed during the ProcessMaker installation when the MySQL password contains a character that is not a letter or a number, like: @ # $% ^ ( /. Warning: arraypop expects parameter 1 to be array, boolean given in /srv/processmaker/processmaker/gulliver/thirdparty/creole/ Creole.php on line 314 Please change/reset your and try to install ProcessMaker again. This is a known issue that will be fixed in ProcessMaker 3.2.
Disabling ONLYFULLGROUPBY mode ProcessMaker does not support ONLYFULLGROUPBY mode, which is enabled by default in MySQL 5.7.5 and later. For instructions, see.